
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic health condition that can affect your physical health and your mental wellbeing. It is understandable that the ongoing physical symptoms such as chronic pain, fatigue and disturbed sleep can cause distress and affect your mood.
Anxiety and depression are common in people with PsA. The good news is that there are effective treatments both for PsA and for anxiety and depression. With careful management, the symptoms of anxiety and depression can be treated along with the symptoms of PsA so you can live as well as possible.
Managing anxiety and depression can greatly improve people’s wellbeing and quality of life as well as their arthritis and their attitude towards it.
PsA and emotions
Many people think that arthritis only affects older people. This is not true.
PsA can occur at any age including in children and young adults. It is not great news to find out you have a chronic health condition and it is not surprising that people can have negative thoughts and emotions such as a sense of loss or distress.
These thoughts and emotions along with decreased participation in enjoyable activities can lead to the development of stress, anxiety and depression (see Figure 1). As a person living with arthritis you need to take care of both your physical health and your mental health and with the right management plan you can live well with arthritis.
Figure One: Chronic pain and mental wellbeing.
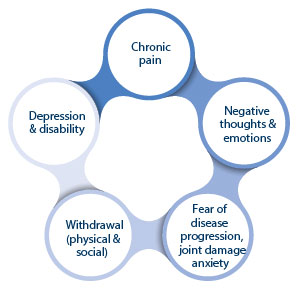
Figure 1: Chronic pain and mental wellbeing
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is more than just feeling stressed or worried. While stress and anxious feelings are a common response to a situation where we feel under pressure, they usually subside once the stressful situation has passed.
Anxiety is when these anxious feelings don’t go away and are ongoing. Often existing without any particular reason or cause. It’s a serious condition that makes it hard to cope with daily life. For someone experiencing anxiety, these feelings can’t be easily controlled.
Many people with anxiety have symptoms of more than one type of anxiety disorder, including depression. Anxiety is common and the sooner you get help, the sooner you can begin to recover.
Signs of anxiety
The symptoms of anxiety are not always obvious as they often develop over time. Given we all experience some anxiety at different points in time, it can be hard to know how much is too much. Normal anxiety tends to be limited in duration and connected with some stressful situation or event such as a job interview.
The type of anxiety experienced by people with an anxiety disorder is more frequent or persistent. It is not always connected to an obvious challenge and impacts on their quality of life and day-to-day functioning. While each anxiety condition has its own unique features, there are some common symptoms including:
- Physical: panic attacks, hot and cold flushes, racing heart, tightening of the chest, quick breathing, restlessness, or feeling tense, wound up and edgy.
- Psychological: excessive fear, worry, unhelpful thoughts, or obsessive thinking.
- Behavioural: avoidance of situations that make you feel anxious which can impact on study, work or social life.
There are effective treatments available for anxiety. For more information on anxiety and treatments visit beyondblue.
What is depression?
While we all feel sad, moody or low from time to time, some people experience these feelings intensely, for long periods of time (weeks, months or even years) often without any apparent reason. Depression is more than just a low mood – it’s a serious condition that has an impact on both physical and emotional wellbeing.
Depression affects how you feel about yourself and makes life more difficult to manage from day-to-day. You may lose interest in work, hobbies and doing things you normally enjoy. You may lack energy, have difficulty sleeping or sleep more than usual, feel anxious or irritable, or find it hard to concentrate.
The encouraging news is that there are a range of treatments, health professionals and services available to help with depression as well as information on how you can help yourself.
Signs of depression
You may be depressed if you have felt sad, down or miserable most of the time for more than two weeks or have lost interest or pleasure in usual activities and have also experienced some of the signs and symptoms in the list below.
It’s important to remember that we all experience some of these symptoms from time to time, and it may not necessarily mean you’re depressed. Equally, not everyone who is experiencing depression will have all of these symptoms. The symptoms will not provide a diagnosis – for that you need to see a health professional – but they can be used as a guide as to when you should seek help.
Some common symptoms of depression include:
- not going out anymore, loss of interest in enjoyable activities
- withdrawing from close family and friends
- being unable to concentrate and not getting things done at work or school
- feeling overwhelmed, indecisive and lacking in confidence
- increased alcohol and drug use
- loss or change of appetite and significant weight loss or gain
- trouble getting to sleep, staying asleep and being tired during the day
- feeling worthless, helpless and guilty
- increased irritability, frustration and moodiness
- feeling unhappy, sad or miserable most of the time
- thoughts such as, ‘I’m a failure’, ‘life’s not worth living’, ‘people would be better off without me’.
It is important to understand that for people with PsA, some of the above symptoms may be the physical symptoms of your arthritis and not necessarily due to depression. So it is vital to discuss how you are feeling with your GP or rheumatologist rather than try and go it alone.
As with anxiety, there are effective treatments available for depression. For more information on depression and treatments visit beyondblue.
What are the links between anxiety, depression and arthritis?
Around three million Australians are living with depression or anxiety. One in five women and one in eight men will experience depression at some time in their life. On average, one in four people will experience anxiety.
Research indicates there is a link between anxiety, depression and arthritis. As is the case with other chronic illnesses, research shows that people with arthritis are more likely to also have anxiety and/or depression. Up to a third of people with arthritis may be clinically depressed. Anxiety is more common in people living with arthritis than those without arthritis and is more common than depression in people with arthritis. For example, one study found that up to seven in ten people with inflammatory arthritis also had anxiety.
If left untreated, arthritis and depression, can impact greatly on a person’s ability to keep active and enjoy life. When arthritis and depression coexist, a person’s ability to function in everyday life, socially and at work or study is often impaired.
People whose arthritis is well controlled are less likely to be depressed than people whose arthritis is not well controlled. In addition, people without depression achieve better control of their arthritis than people with depression.
Managing anxiety and depression can greatly improve a person's wellbeing and quality of life. As well as improve their arthritis and their attitude towards it. People with anxiety and/or depression can find it difficult to take the first step in seeking help. They may need the support of family, friends and a health professional.
What are the treatments for anxiety and depression?
Talking and emotional support can help to reduce the stress of coping with PsA but in some cases, professional help may be needed. There is no one proven way that people recover from anxiety or depression and it’s different for everybody. However, there is a range of effective treatments and health professionals and other support people who can help you on the road to recovery.
There are also many things that people can do to help themselves recover and stay well. The important thing is finding the right treatments and the right health professionals and support team that work for you.
Different types of anxiety or depression require different types of treatment. This may include lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, healthy eating and adequate sleep, family and peer support, and psychological therapy for mild-moderate anxiety and depression, through to more specialised psychological and medical treatments for severe depression and/or anxiety. What’s important is getting the treatment and support that’s right for your condition and situation.
The treatment for anxiety and depression in someone with PsA involves a coordinated approach managed by your GP that monitors and treats the symptoms of anxiety, depression and arthritis.
Psychological treatments
Psychological treatments can help you change your thinking patterns and improve your coping skills, so you’re better equipped to deal with life’s stresses and conflicts.
As well as supporting your recovery, psychological therapies can also help you stay well by identifying and changing unhelpful thoughts and behaviour. These treatments help build skills in coping with stressful life circumstances and can be provided by a psychologist, psychiatrist or other trained health professional.
- Cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective treatments for people with anxiety and depression. It works to change your thoughts and behaviour by teaching you to think rationally about common difficulties, helping you to shift negative or unhelpful thought patterns and reactions to a more realistic, positive and problem-solving approach.
- Interpersonal therapy (IPT) is also effective for treating depression and some types of anxiety. It helps people find new ways to get along with others and to resolve losses and conflict in relationships.
Medication
Antidepressant medication is sometimes used along with psychological therapies to treat moderate to severe depression and some anxiety conditions.
Making a decision about which antidepressant is best for a person can be complex. The decision will be made in consultation with your doctor, after careful assessment and consideration. The doctor should discuss differences in effects, possible side effects of medications and whether they can interact with other medications you are taking. Stopping antidepressant medication should only be done gradually with a doctor’s recommendation and under supervision.
A doctor or treating health professional will consider several factors when suggesting the most suitable treatment. Regular contact with, and ongoing assessment by a doctor to check that treatments are working effectively is an important part of becoming and staying well. Most people taking medication will also benefit from psychological therapies which will reduce the likelihood of anxiety or depression coming back after the person has stopped taking the medication.
Exercise and staying active can also help
For people living with PsA, not only will exercise help you build your physical fitness, it has also been shown to help build your mental fitness. Being active and regularly exercising helps reduce the symptoms of depression.
Please talk with your doctors or a physiotherapist to work out what exercises will be most appropriate for you. A mix of aerobic exercises such as swimming or walking, muscle strengthening and balance exercises is often helpful. In general, any activity that works your muscles a bit harder or makes you ‘puff’ a little, without increasing your pain or other symptoms, will be beneficial. Most importantly, do activities that you enjoy and make them part of your everyday routine.
Who can assist?
Most of us wouldn’t try and treat a broken leg ourselves. But when it comes to our mental health, we sometimes think we can fix things on our own, or hope the issue just goes away by itself.
That’s where health professionals come in. There are plenty of effective treatments for anxiety and depression, and the sooner you seek support, the sooner you can recover.
A general practitioner (GP) is the best starting point for someone seeking professional help. Your GP can:
- make a diagnosis
- check for any physical health problems or medication that may be contributing to your condition or may affect your treatment
- provide information and discuss available treatments taking your preferences into account
- work with you to draw up a Mental Health Care Plan so you can get a Medicare rebate for psychological treatment (if appropriate)
- provide support, brief counselling or, in some cases, more specialised talking therapy
- prescribe medication
- refer you to a mental health specialist such as a psychologist or psychiatrist (if appropriate).
- provide information and support to family members, if you agree
- schedule regular appointments to check how you are going.
It is recommended that you see your regular GP if you have one, or another GP in the same clinic, as they will be aware of your arthritis and any other health issues.
You should also let your rheumatologist, or the specialist managing your arthritis treatment, know how you are feeling and if you have anxiety or depression.
Psychologists are health professionals who provide psychological therapies such as cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy (IPT). Clinical psychologists and other psychologists are not doctors and cannot prescribe medication in Australia.
Psychiatrists are doctors who have undergone further training to specialise in the assessment, diagnosis and treatment of mental health problems. They can make medical and psychiatric assessments, conduct medical tests, provide therapy and prescribe medication. Psychiatrists often use psychological treatments such as CBT, IPT and/or medication. If the depression or anxiety is severe and hospital admission is required, a psychiatrist will be in charge of your treatment.
Mental health nurses are nurses who have undertaken specialist training to care for people with mental health conditions. They work in specialist mental health services and with psychiatrists and GPs to review your mental health, monitor medication or other treatment recommended by your GP or psychiatrist, and provide information about mental health conditions and treatment. Some nurses have training in psychological therapies.
Accredited mental health social workers specialise in working with and treating mental health conditions. They draw on a range of theories and therapeutic approaches to work holistically with people to support their recovery and help them to effectively manage or change the situations that may contribute to mental health conditions. Many accredited mental health social workers can provide focused psychological strategies, such as cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), relaxation training, psycho-education and interpersonal skills training. Oncology social workers have experience in supporting people with cancer, and their families.
Occupational therapists in mental health help people who have difficulty functioning because of a mental health condition to participate in normal, everyday activities. Mental health occupational therapists also provide focused psychological self-help strategies, including relaxation training.
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander mental health workers understand the health issues of Indigenous people and what is needed to provide culturally safe and accessible services. Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander mental health workers are health workers who work specifically in the mental health area and have specific mental health qualifications. Support provided by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander mental health workers might include, but not be limited to, screening, assessment, referrals, case management, transport to and attendance at specialist appointments, education, improving access to mainstream services, advocacy, counselling, support for family and acute distress response.
The cost of treatment from a mental health professional varies. However, in the same way that you can get a Medicare rebate when you see a doctor, you may also be able to get part or all of the consultation fee subsidised when you see certain mental health professionals for treatment of anxiety or depression. You will need to see your GP before making the appointment to have a Mental Health Care Plan drawn up for you.
Visit the beyondblue to find out more information on getting support and how much it costs.
To find a mental health practitioner in your area, visit beyondblue or call the their Support Service on 1300 22 4636.
Helpful strategies and tips
- Learn about anxiety, depression and arthritis and how these conditions interact.
- Learn how to distinguish the symptoms of arthritis from the symptoms of anxiety or depression.
- Plan with your doctor – have a mental health care plan.
- Visit your doctor regularly to review your PsA and mental health management.
- Use your arthritis medicine as prescribed. Talk to your doctor about possible barriers to taking medicine, such as cost, organisation or planning, as well as what to do if your PsA worsens.
- Get help, support and encouragement from family and friends and have them help you to follow your PsA and mental health plans.
- Learn relaxation techniques.
- Get involved in social activities.
- Stay active and exercise under the supervision of a doctor.
- Eat healthily and include a wide variety of nutritious foods.
- Limit your substance use (including alcohol, tobacco and coffee).
How family and friends can help
When a person has arthritis and anxiety or depression, it can affect family and friends. It’s important for family and friends to look after their own health as well as supporting or looking after the person who has arthritis.
- Learn about PsA, anxiety and depression and their symptoms to help you recognise warning signs.
- Encourage the person to go to the doctor if their arthritis, anxiety or depression gets worse. Make sure you seek help if you think you need it, too.
- Support the person by helping them to follow their arthritis and mental health plans. Gently remind the person to take their arthritis, anxiety and depression medication regularly and to attend all their medical appointments.
- Encourage the person with arthritis to do things that they would normally enjoy.
- Look after your own health by eating well, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep and doing things that you enjoy, too.
CONTACT YOUR LOCAL ARTHRITIS OFFICE FOR MORE INFORMATION AND SUPPORT SERVICES.










